The Automotive Windscreen is an engineering marvel designed for both style and substance. Over the lifetime of an Automobile, Truck or SUV, the all-important Windscreen Glass is engineered to take a beating from structural support and handling design stresses while driving, to providing UV protection and safety performance for vehicle occupants in the event of a mishap.
The Windscreen isn’t invulnerable however; there are a host of roadside hazards that can nip, chip or even crack the modern day Windscreen.
This article takes a closer look at how Windscreen repair technicians approach such damage, when considering the option of repairing a Windscreen, rather than replacing it.
The Windscreen, for your information, is made up of laminated Automotive Glass. This is actually two layers of glass, sandwiched around a thin barrier, that when safely heated becomes Automotive Safety Glass. The barrier in between the Glass, called the lamination helps to hold broken pieces of Glass together in the event of a mishap.
Windscreen repair is the process of injecting a curable resin into the outer layer of Glass on a chipped Windscreen to restore that layer of Glass, and while that may sound relatively simple, there are a number of factors to consider when identifying and executing a successful repair.
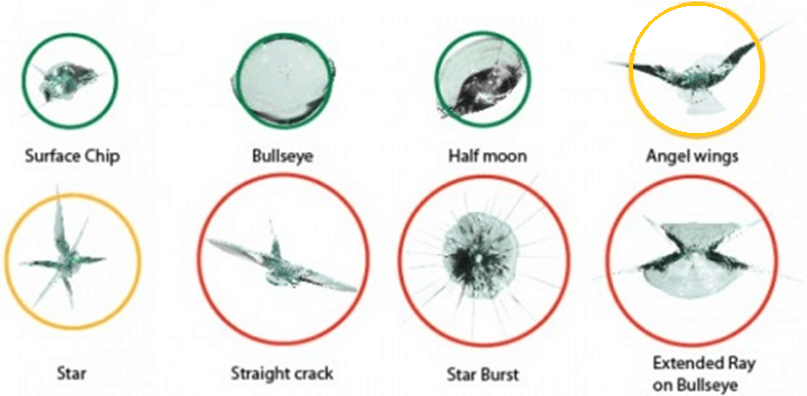
Let’s start by looking at what a repair technician looks for when assessing what can reasonably be repaired. Traditionally, breaks in a Windscreen have fallen under the following eight descriptors;